Keeping inventory small business – In the realm of small business, keeping inventory plays a pivotal role in determining success. By implementing effective inventory management strategies, businesses can minimize waste, maximize efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of inventory management, providing invaluable insights and practical techniques to help small businesses optimize their stock.
From understanding lean inventory principles to leveraging technology for efficient inventory control, this guide covers all aspects of inventory management. Discover how to reduce excess inventory, forecast demand, and tailor inventory strategies to specific business types. Real-world case studies provide tangible examples of businesses that have successfully implemented inventory management solutions.
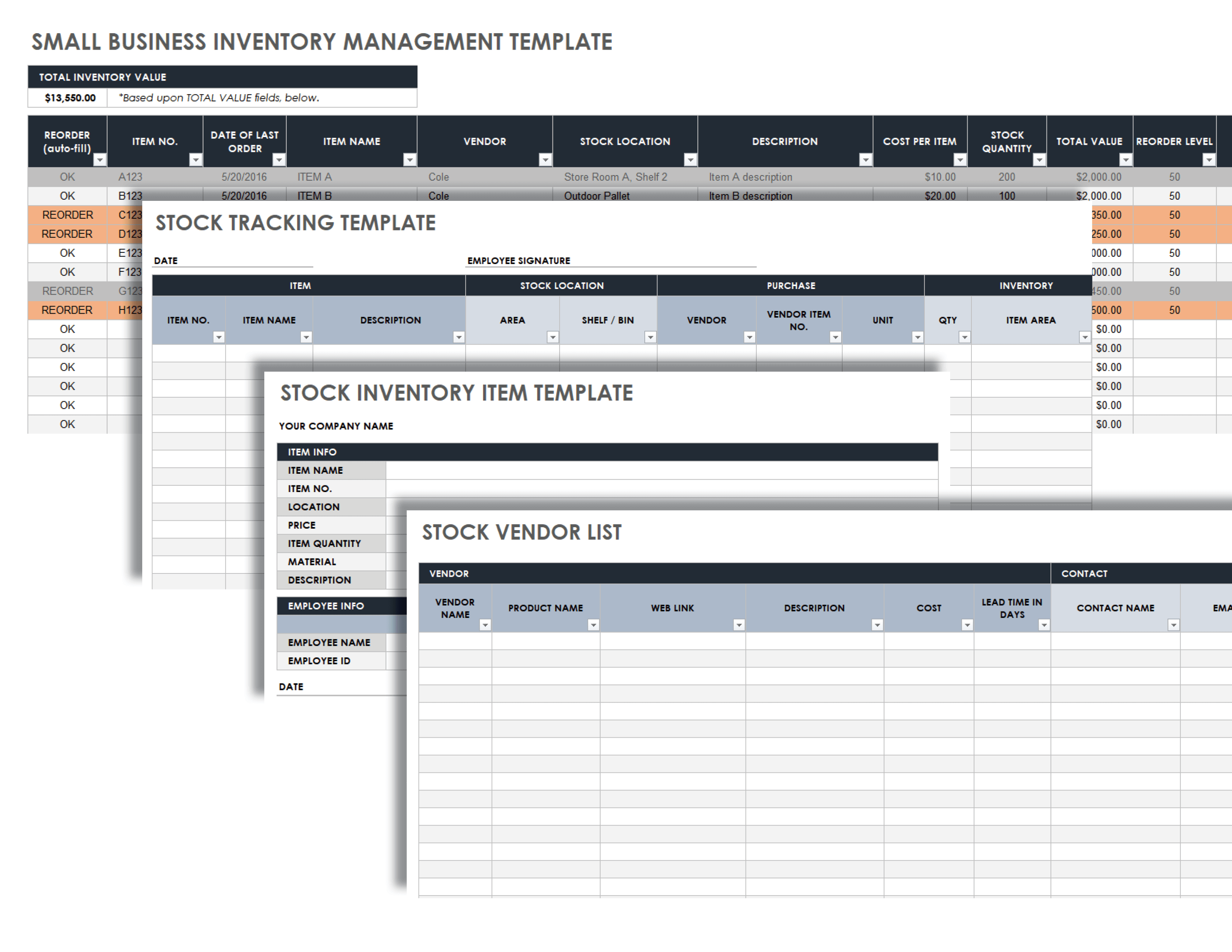
Inventory Management Best Practices
Effective inventory management is crucial for small businesses to optimize cash flow, minimize waste, and enhance efficiency. Lean inventory management principles provide a framework for achieving these goals.
Lean inventory management emphasizes holding only the necessary inventory levels to meet current demand. This approach reduces carrying costs, minimizes obsolescence risks, and improves cash flow.
Optimizing Inventory Levels
- Conduct regular inventory audits: Track inventory levels accurately and identify discrepancies to minimize overstocking or understocking.
- Use inventory forecasting tools: Predict future demand based on historical data and market trends to determine optimal inventory levels.
- Implement safety stock: Maintain a buffer inventory to mitigate unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply chain disruptions.
Just-in-Time Inventory Systems
Just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems aim to receive inventory only when it is needed for production or sale. This approach minimizes inventory carrying costs and reduces the risk of obsolescence.
- Establish strong supplier relationships: Collaborate with suppliers to ensure timely and reliable deliveries.
- Implement Kanban systems: Use visual cues to trigger inventory replenishment when needed.
- Cross-train employees: Empower employees to perform multiple tasks to increase flexibility and reduce lead times.
Inventory Control Strategies: Keeping Inventory Small Business
Effective inventory control is crucial for small businesses to optimize stock levels, minimize waste, and improve profitability. Utilizing inventory control software can streamline operations, provide real-time data, and automate tasks.
Inventory Control Software
- Automates inventory tracking, reducing errors and saving time.
- Provides real-time visibility into stock levels, enabling informed decision-making.
- Generates reports and analytics to identify trends, optimize ordering, and reduce overstocking.
Inventory Control Techniques
Various techniques can help small businesses manage inventory efficiently:
ABC Analysis
Classifies inventory items into three categories based on their value and usage:
- A-items: High-value, frequently used items requiring close monitoring and tight control.
- B-items: Moderate-value items with regular usage, requiring periodic monitoring.
- C-items: Low-value, infrequently used items requiring minimal attention.
FIFO (First-In, First-Out)
Assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first, preventing spoilage and ensuring product freshness.
Reorder Points and Safety Stock Levels
Establishing reorder points and safety stock levels helps prevent stockouts and ensures adequate inventory on hand:
- Reorder point: The inventory level at which a new order should be placed.
- Safety stock: Additional inventory held to buffer against unexpected demand fluctuations or delays.
Calculating these levels requires consideration of factors such as demand patterns, lead times, and desired service levels.
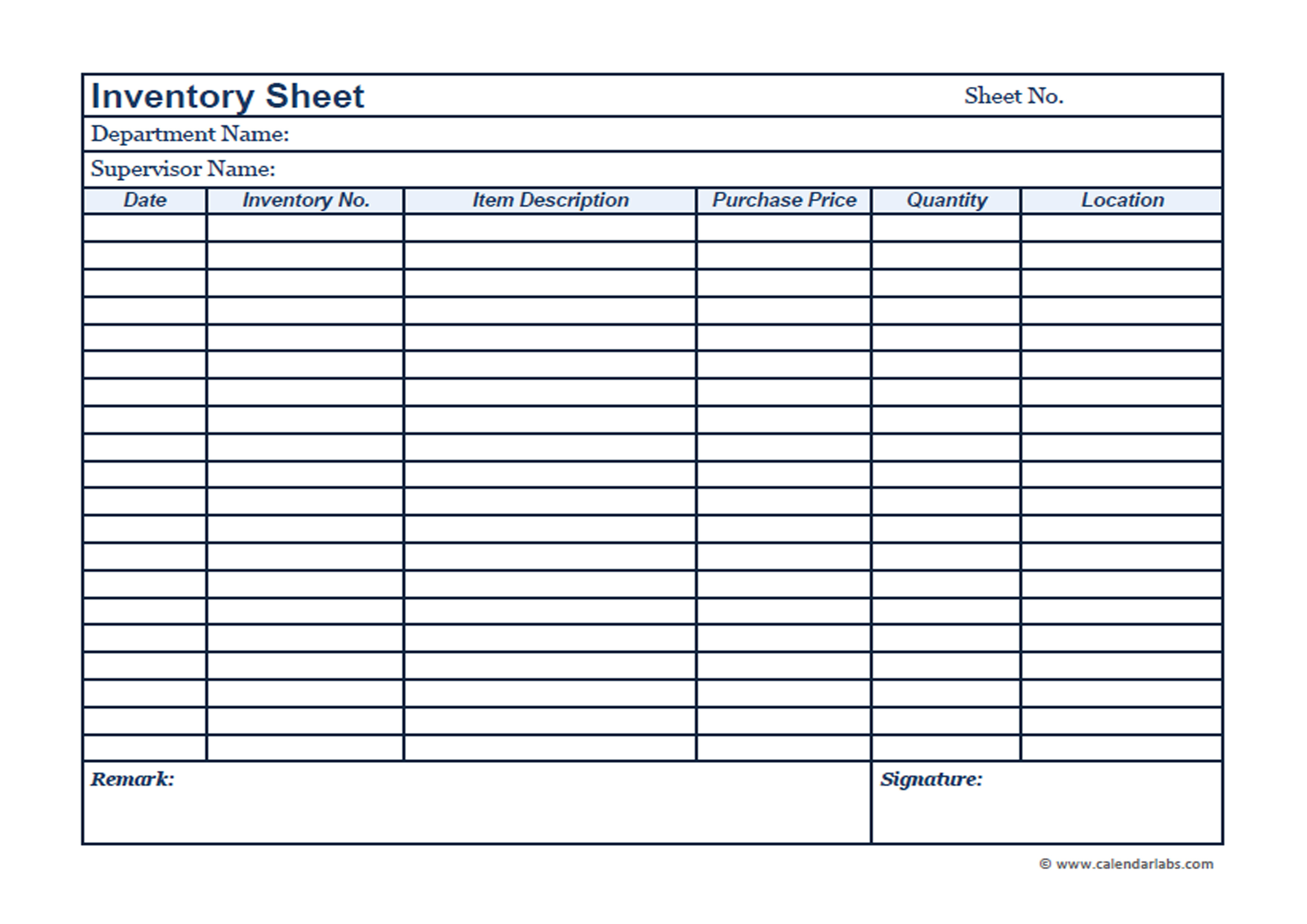
Inventory Tracking Methods
Maintaining accurate inventory records is crucial for small businesses. Implementing a robust inventory tracking system allows you to monitor stock levels, prevent overstocking or understocking, and optimize your operations.
Manual Inventory Tracking
For businesses with a small inventory, manual tracking using spreadsheets or databases can be an effective option. Spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets offer customizable templates for tracking inventory data, including product name, quantity, unit cost, and reorder point.
Barcode Scanners and RFID Technology
For larger businesses or those with a high volume of inventory, barcode scanners and RFID technology provide efficient and accurate inventory tracking solutions. Barcode scanners use optical technology to read barcodes attached to products, while RFID tags use radio waves to transmit data about products.
Tips for Accurate Inventory Records
- Regularly conduct physical inventory counts to verify the accuracy of your records.
- Establish clear inventory policies and procedures to ensure consistency in tracking and handling.
- Use inventory management software to automate tracking and reduce the risk of errors.
- Train staff on inventory management best practices and ensure they understand their responsibilities.
- Implement cycle counting, where a portion of the inventory is counted and verified regularly to identify any discrepancies.
Inventory Reduction Techniques
Excess inventory can tie up cash flow and lead to losses if not managed properly. Here are some strategies for reducing excess inventory:
Markdown Sales
Markdown sales can help move excess inventory quickly. By offering discounts, businesses can entice customers to purchase items they might not otherwise consider. Markdown sales should be used strategically to avoid devaluing products or damaging brand reputation.
Vendor Negotiations, Keeping inventory small business
Negotiating with vendors can help reduce inventory levels by adjusting order quantities, lead times, and return policies. Businesses can work with vendors to establish consignment agreements or implement vendor-managed inventory systems to reduce the risk of overstocking.
Inventory Shrinkage
Inventory shrinkage refers to the loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or administrative errors. Minimizing inventory shrinkage is crucial for maintaining accurate inventory records and preventing losses. Implementing strong security measures, conducting regular inventory audits, and using technology to track inventory can help reduce shrinkage.
Inventory Forecasting
Inventory forecasting techniques help businesses predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. By analyzing historical sales data, seasonality, and market trends, businesses can optimize inventory levels to meet customer demand without overstocking.
Inventory Optimization for Different Business Types
Different types of small businesses face unique challenges in managing their inventory. By understanding these challenges and implementing customized solutions, businesses can optimize their inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Retail Businesses
Retail businesses often struggle with managing inventory due to factors such as seasonality, product lifecycles, and customer demand fluctuations. To optimize inventory, retailers can implement strategies such as:
- Using demand forecasting tools to predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
- Implementing a just-in-time inventory system to reduce carrying costs and minimize the risk of obsolete inventory.
- Offering promotions and discounts to clear out excess inventory.
Manufacturing Businesses
Manufacturing businesses face challenges in managing inventory due to the need to balance production schedules, raw material availability, and finished goods inventory levels. To optimize inventory, manufacturers can implement strategies such as:
- Using materials requirement planning (MRP) systems to plan and schedule production based on demand.
- Implementing kanban systems to manage inventory levels and ensure a smooth flow of materials through the production process.
- Outsourcing non-core inventory management tasks to third-party providers.
E-commerce Businesses
E-commerce businesses face challenges in managing inventory due to factors such as rapid order fulfillment, limited storage space, and the need to manage multiple sales channels. To optimize inventory, e-commerce businesses can implement strategies such as:
- Using drop shipping to reduce inventory carrying costs and storage space requirements.
- Implementing a multi-channel inventory management system to track inventory levels across multiple sales channels.
- Offering free shipping or other incentives to encourage customers to purchase items that are in excess inventory.
Impact of Seasonality and Product Lifecycles on Inventory Management
Seasonality and product lifecycles can have a significant impact on inventory management. Businesses need to adjust their inventory levels accordingly to meet seasonal demand fluctuations and to account for the different stages of a product’s lifecycle.
During peak seasons, businesses may need to increase inventory levels to meet increased demand. During off-seasons, businesses may need to reduce inventory levels to minimize carrying costs and the risk of obsolete inventory.
Businesses also need to consider the product lifecycle when managing inventory. Products in the introduction stage may require higher inventory levels to meet initial demand. As products move through the growth and maturity stages, inventory levels can be reduced. Products in the decline stage may require clearance sales or other strategies to reduce inventory levels.
Inventory Management Case Studies

Numerous small businesses have reaped significant benefits from implementing effective inventory management strategies. Here are a few real-world examples:
Case Study: XYZ Electronics
- Challenge: Overstocking, leading to high storage costs and product obsolescence.
- Solution: Implemented a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system, reducing inventory levels by 30%.
- Benefits: Saved 15% on storage costs, reduced product obsolescence by 25%, and improved customer satisfaction due to faster order fulfillment.
Case Study: ABC Retail
- Challenge: Inaccurate inventory records, resulting in lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
- Solution: Implemented a cloud-based inventory management system with real-time tracking.
- Benefits: Increased inventory accuracy by 90%, reduced lost sales by 10%, and improved customer satisfaction through accurate order processing.
Ending Remarks
By embracing the principles and techniques Artikeld in this guide, small businesses can transform their inventory management practices. Optimized inventory levels, reduced waste, and improved efficiency will empower businesses to thrive in today’s competitive market. Keeping inventory small business is not merely about managing stock; it’s about unlocking growth, profitability, and customer delight.
Quick FAQs
What are the key principles of lean inventory management?
Lean inventory management focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency by reducing inventory levels, implementing just-in-time systems, and optimizing stock replenishment.
How can inventory control software benefit small businesses?
Inventory control software automates inventory tracking, provides real-time visibility into stock levels, and facilitates efficient order management, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
What are some effective inventory reduction techniques?
Effective inventory reduction techniques include markdown sales, vendor negotiations, and implementing inventory forecasting to prevent overstocking.