Business inventory tracking, a cornerstone of supply chain management, empowers businesses with real-time visibility into their stock levels. It plays a pivotal role in optimizing inventory levels, minimizing waste, and ensuring seamless operations.
From manual methods to sophisticated automated systems, businesses have a plethora of options to track their inventory. This article delves into the intricacies of inventory tracking, exploring its significance, techniques, and strategies for optimizing inventory levels.
Inventory Tracking Fundamentals
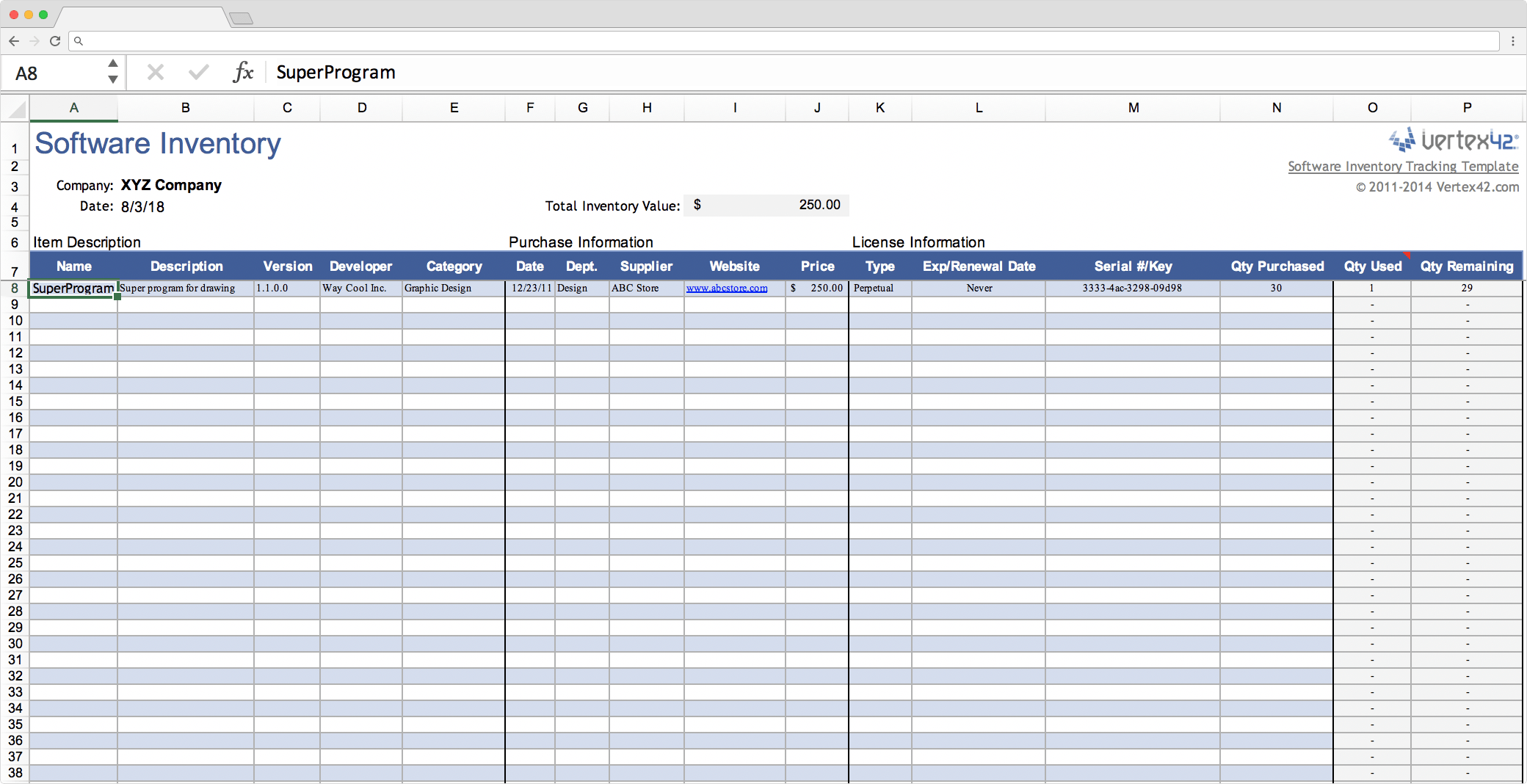
Inventory tracking is a crucial aspect of supply chain management that involves monitoring and managing the stock levels of goods and materials within a business. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring that businesses have the right inventory at the right time and place to meet customer demand while minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Types of Inventory Tracking Methods
There are various inventory tracking methods that businesses can employ, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the common methods include:
- Manual Inventory Tracking:This method involves physically counting and recording inventory levels using pen and paper or spreadsheets. While it is simple and cost-effective, it can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Automated Inventory Tracking:This method uses technology, such as barcode scanners or RFID tags, to automate the process of inventory tracking. It provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, reduces errors, and streamlines inventory management.
- Periodic Inventory Tracking:This method involves counting inventory levels at regular intervals, such as monthly or quarterly. It is less labor-intensive than manual inventory tracking but provides less frequent updates on inventory levels.
- Perpetual Inventory Tracking:This method involves continuously updating inventory levels as transactions occur. It provides real-time visibility into inventory levels but requires a more robust system and can be more complex to implement.
Inventory Management Techniques
Inventory management techniques encompass both manual and automated methods designed to track and control inventory levels. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each approach can help businesses optimize their inventory management processes.
Manual Inventory Tracking Methods
Manual inventory tracking involves physical counting and recording of inventory items. It is a simple and cost-effective method, suitable for small businesses with limited inventory.
- Cycle counting:Periodic physical counts of a portion of inventory to identify discrepancies.
- Periodic inventory:Complete physical count of inventory at regular intervals, typically at the end of a month or quarter.
- Spot checks:Random inspections of inventory to verify accuracy.
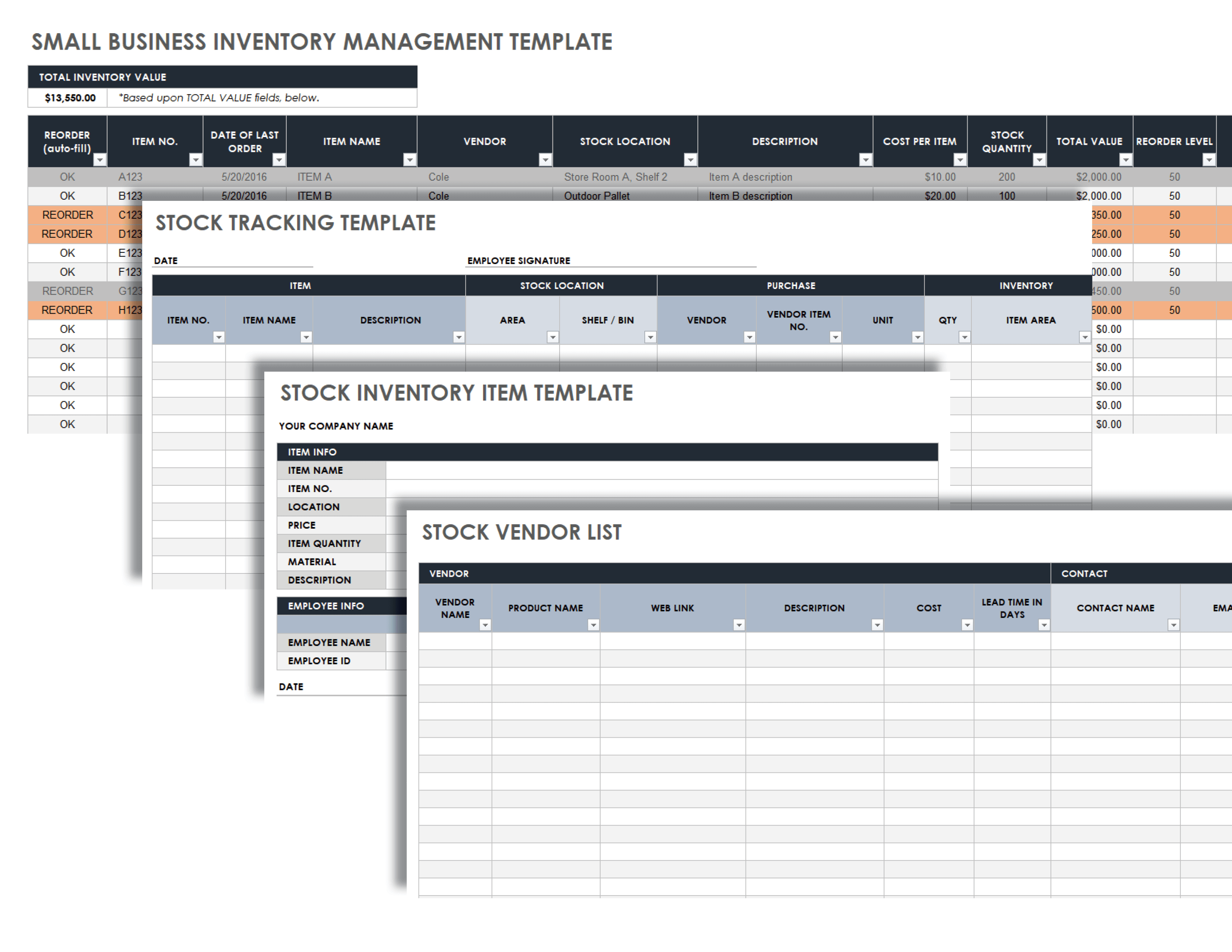
Automated Inventory Tracking Systems
Automated inventory tracking systems use technology to automate inventory tracking processes, providing real-time visibility and accuracy.
- Radio frequency identification (RFID):Uses radio waves to track inventory items tagged with RFID chips.
- Barcode scanners:Scan barcodes on inventory items to record and update inventory levels.
- Inventory management software:Comprehensive software solutions that provide features for inventory tracking, order management, and reporting.
Examples of Inventory Management Software
- NetSuite:Cloud-based inventory management software with robust features for businesses of all sizes.
- SAP Business One:ERP software with integrated inventory management capabilities.
- QuickBooks:Accounting software with inventory tracking features for small businesses.
Inventory Data Analysis
Inventory data analysis is crucial for businesses to optimize inventory management, reduce costs, and enhance profitability. It involves tracking inventory levels, identifying trends and patterns, and making informed decisions to ensure optimal stock levels.Tracking inventory levels is essential for preventing stockouts and overstocking.
Businesses can use various methods, such as physical inventory counts, perpetual inventory systems, and inventory management software, to monitor inventory levels in real-time.By analyzing inventory data, businesses can identify trends and patterns in demand, sales, and stock levels. This analysis helps them forecast future demand, adjust inventory levels accordingly, and optimize supply chain operations.
Inventory Optimization Strategies
Inventory optimization aims to balance the risks of understocking and overstocking to minimize inventory costs while meeting customer demand. This involves techniques such as forecasting, setting safety stock levels, and implementing inventory optimization algorithms.Inventory forecasting helps predict future demand, enabling businesses to adjust their inventory levels accordingly.
Accurate forecasting reduces the likelihood of stockouts and minimizes excess inventory. Techniques like time series analysis, moving averages, and machine learning are commonly used for forecasting.
Inventory Optimization Algorithms
Various algorithms have been developed to optimize inventory levels. Some common ones include:
Fixed Order Quantity (FOQ)
Determines the optimal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs, considering ordering costs and holding costs.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Similar to FOQ, but assumes constant demand and lead time.
Periodic Review System
Reviews inventory levels at regular intervals and orders enough to reach a target level.
Just-in-Time (JIT)
Aims to minimize inventory by ordering materials only when needed, reducing holding costs and waste.
Real-World Applications
Inventory tracking plays a crucial role in various industries, enabling businesses to optimize their supply chains, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Across retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and e-commerce, effective inventory management ensures that the right products are available at the right time, minimizing stockouts and overstocking.
Challenges and Best Practices
- Forecasting demand accurately to avoid overstocking or understocking
- Balancing inventory levels to meet customer needs while minimizing carrying costs
- Implementing robust inventory tracking systems that provide real-time visibility and data accuracy
- Establishing clear inventory management policies and procedures to ensure consistency and accountability
li>Leveraging technology such as RFID tags, barcodes, and inventory management software to automate processes and improve efficiency
Case Studies
Retail: Walmart’s RFID Implementation
Walmart successfully implemented RFID technology in its stores to improve inventory accuracy, reduce shrink, and enhance customer experience. The RFID tags allowed for real-time tracking of inventory, enabling Walmart to optimize stock levels and provide better product availability.
Manufacturing: Toyota’s Just-in-Time Inventory System
Toyota’s Just-in-Time inventory system revolutionized manufacturing by minimizing inventory levels and improving production efficiency. By closely coordinating with suppliers and implementing a pull-based production system, Toyota reduced waste and increased profitability.
Healthcare: Hospital Inventory Management
Effective inventory management in hospitals is critical for patient safety and operational efficiency. Hospitals use inventory tracking systems to monitor medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and equipment, ensuring that essential items are available when needed.
Future Trends in Inventory Tracking
![]()
The future of inventory tracking is shaped by emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), promising significant advancements in inventory management.
Impact of AI and IoT on Inventory Management, Business inventory tracking
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of inventory data to identify patterns, predict demand, and optimize stock levels. IoT sensors can track inventory movement in real-time, providing accurate and up-to-date visibility into inventory levels.
Advanced Inventory Tracking Techniques
- Automated Inventory Management:AI-powered systems can automate inventory replenishment, reducing manual tasks and improving efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics:AI algorithms can forecast demand based on historical data and external factors, enabling businesses to optimize inventory levels and avoid stockouts.
- RFID Technology:Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags can track individual items, providing granular visibility and reducing errors.
Implications for Businesses
These advancements have profound implications for businesses, including:
- Improved Inventory Accuracy:Real-time tracking and data analysis reduce errors and increase inventory accuracy.
- Reduced Costs:Optimized inventory levels and automated processes lower storage and labor costs.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction:Accurate inventory data ensures availability of products, reducing backorders and improving customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The future of inventory tracking is characterized by the integration of advanced technologies, leading to more efficient, accurate, and cost-effective inventory management practices.
Final Thoughts
In the ever-evolving landscape of supply chain management, inventory tracking remains indispensable. By embracing emerging technologies and adopting best practices, businesses can harness the power of inventory tracking to drive efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge.
Questions and Answers: Business Inventory Tracking
What are the benefits of business inventory tracking?
Business inventory tracking offers numerous benefits, including improved stock visibility, reduced waste, optimized inventory levels, enhanced customer service, and better decision-making.
What are the different types of inventory tracking methods?
Businesses can choose from manual inventory tracking methods, such as spreadsheets and physical counts, or automated inventory tracking systems that leverage technology for real-time tracking and data analysis.
How can businesses optimize their inventory levels?
Inventory optimization strategies involve techniques such as demand forecasting, safety stock management, and inventory classification, which help businesses maintain optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing waste.