Inventory management small business – Inventory management is a critical aspect of running a successful small business. It involves the efficient and cost-effective management of the inventory, ensuring the right amount of stock is available to meet customer demand while minimizing waste and loss.
This comprehensive guide will provide small business owners with a deep understanding of inventory management principles, software solutions, optimization strategies, tracking methods, cost management techniques, control and security measures, and industry-specific considerations.
Inventory Management Basics for Small Businesses: Inventory Management Small Business
Inventory management is crucial for small businesses as it helps control the flow of goods, ensuring optimal stock levels and minimizing losses. Effective inventory management practices involve tracking inventory levels, forecasting demand, and optimizing stock replenishment to meet customer needs while minimizing waste.
Common Inventory Management Techniques
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO):Assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, ensuring fresh stock is always available.
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO):Assumes that the newest inventory is sold first, potentially resulting in higher costs due to inflation.
- Just-in-Time (JIT):Aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when needed, reducing storage costs but requiring precise forecasting.
Importance of Inventory Accuracy and Control
Accurate inventory records are essential for effective decision-making. Regular inventory audits help identify discrepancies, prevent stockouts, and ensure optimal stock levels. Proper inventory control systems, such as inventory management software, streamline inventory tracking, reduce errors, and provide real-time visibility into stock levels.
Inventory Management Software Solutions
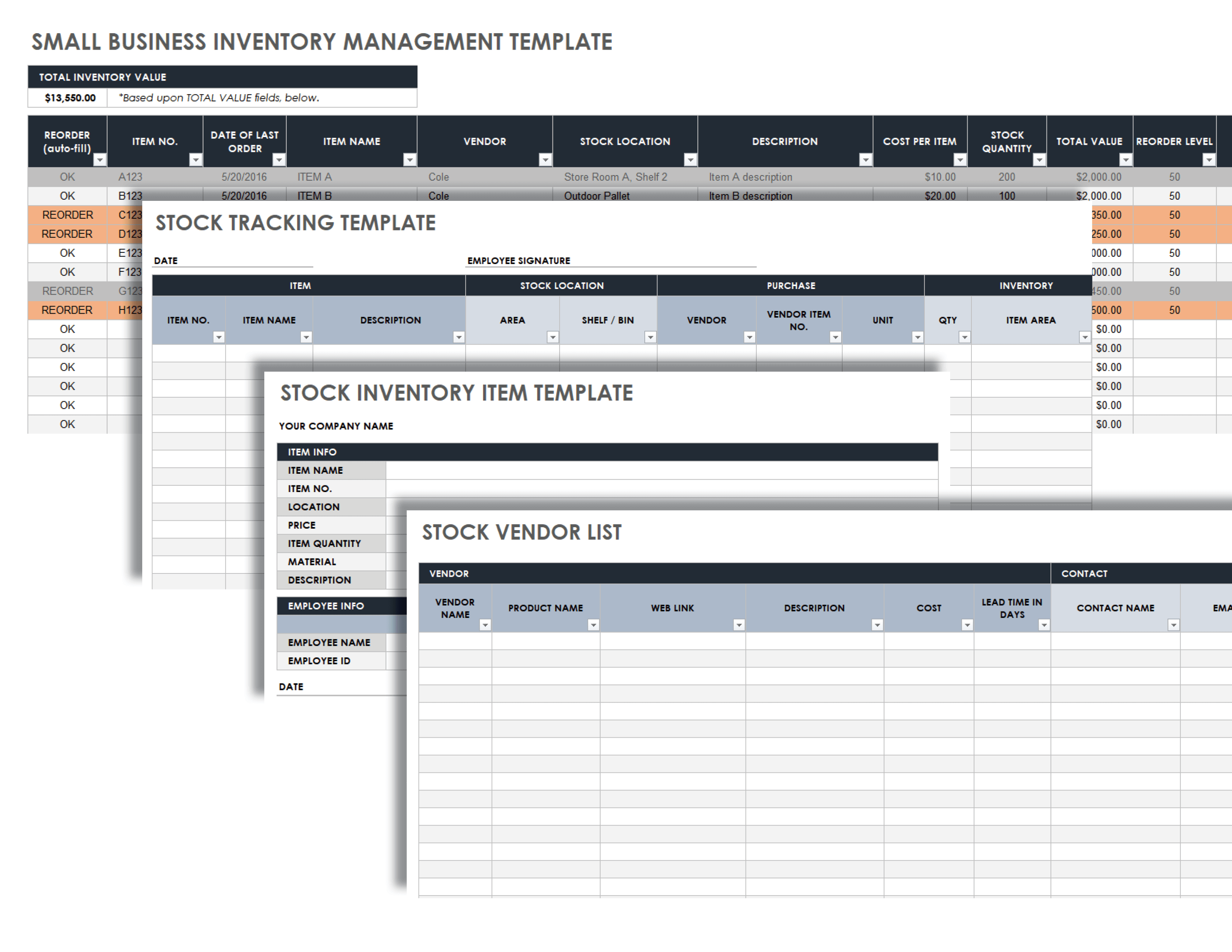
Inventory management software is a valuable tool for small businesses, offering features and benefits that can streamline operations and improve efficiency. From real-time inventory tracking to automated reordering, these solutions provide businesses with the insights and control they need to manage their inventory effectively.
When choosing inventory management software, consider your specific business needs and budget. Some key factors to consider include:
- Number of products and SKUs
- Inventory turnover rate
- Warehouse or storage space
- Budget
Software Options for Small Businesses
Numerous inventory management software options are available for small businesses, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are a few popular choices:
- QuickBooks Commerce: Ideal for small businesses with basic inventory management needs.
- Zoho Inventory: Offers a comprehensive suite of features for small and growing businesses.
- Shopify: An e-commerce platform with built-in inventory management capabilities.
- NetSuite: A cloud-based ERP solution that includes inventory management as part of its suite.
Selecting the Right Software, Inventory management small business
To select the right inventory management software for your business, consider the following steps:
- Identify your business needs:Determine the specific features and functionality you require.
- Research and compare options:Explore different software options and compare their features, pricing, and customer support.
- Get a demo:Request a demonstration to see the software in action and ask questions.
- Implement and train:Once you’ve selected a software, implement it and train your staff on how to use it.
- Maximum Daily Demand is the highest daily demand observed historically.
- Lead Time is the time between placing an order and receiving the goods.
- Safety Factor is a buffer added to account for uncertainties (typically 10-20%).
- Challenges:Fluctuating demand, seasonality, product obsolescence
- Practices:Just-in-time inventory, vendor-managed inventory, RFID technology
- Case Study:Zara’s efficient inventory management system allows for quick response to changing fashion trends and reduced markdowns.
- Challenges:Long lead times, complex supply chains, fluctuating demand
- Practices:Material requirements planning (MRP), safety stock management, lean manufacturing
- Case Study:Toyota’s kanban system has revolutionized inventory management in manufacturing, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Challenges:Perishable goods, regulatory compliance, high-value inventory
- Practices:Inventory control systems, automated dispensing cabinets, RFID technology
- Case Study:The Cleveland Clinic’s inventory management system has improved medication safety and reduced inventory costs.
Inventory Optimization Strategies
Inventory optimization aims to maintain optimal inventory levels, balancing stock availability with cost efficiency. It’s crucial for small businesses to optimize inventory to avoid overstocking (leading to storage costs and potential spoilage) or understocking (resulting in lost sales and customer dissatisfaction).
Safety Stock Calculations
Safety stock is the additional inventory held to buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply. It helps prevent stockouts and ensures business continuity. To calculate safety stock, consider the following formula:“`Safety Stock = (Maximum Daily Demand
Lead Time) + Safety Factor
“`Where:
Forecasting and Demand Planning
Forecasting and demand planning play a vital role in inventory optimization. Accurate forecasts help businesses predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. Techniques like historical data analysis, seasonal adjustments, and market research can enhance forecasting accuracy. Demand planning involves collaborating with sales and marketing teams to anticipate customer needs and align inventory with projected demand.
Inventory Tracking and Monitoring

Effective inventory tracking and monitoring are crucial for small businesses to maintain optimal stock levels, prevent shortages, and reduce waste. Here are some methods and tools to help you keep track of your inventory:
Manual Tracking:This involves using physical methods like spreadsheets or notebooks to record inventory levels. While it’s simple and cost-effective, it can be prone to errors and time-consuming.
Barcode Scanning:Using barcode scanners to track inventory is more efficient and accurate. Scanners read barcodes on products and automatically update inventory records in real-time.
RFID Technology:Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags are attached to products and emit signals that can be detected by RFID readers. This allows for automatic and continuous inventory tracking, even in large warehouses.
Inventory Reports and Dashboards:These tools provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing businesses to monitor stock levels, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Dashboards often include customizable widgets that display key inventory metrics.
Regular Inventory Audits
Regular inventory audits are essential for verifying the accuracy of inventory records. This involves physically counting inventory and comparing it to the records. Audits help identify discrepancies, prevent shrinkage, and ensure inventory levels are accurate.
Inventory Management for Specific Industries
Every industry has its unique inventory management challenges and requirements. Understanding these nuances is crucial for businesses to optimize their inventory strategies and streamline their operations.
This section explores the specific inventory management challenges faced by different industries and provides industry-specific examples and case studies of successful inventory management implementations.
Retail Industry
Retail businesses deal with a vast and diverse range of products, each with varying demand patterns and shelf lives. Managing inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing waste and spoilage is a constant challenge.
Manufacturing Industry
Manufacturers must balance the need for raw materials and finished goods inventory with production schedules and customer orders. Efficient inventory management is essential for optimizing production processes and minimizing downtime.
Healthcare Industry
Healthcare providers face the challenge of managing critical medical supplies and pharmaceuticals with varying shelf lives and strict regulatory requirements. Accurate and timely inventory management is essential for patient safety and cost-effectiveness.
End of Discussion
By implementing effective inventory management practices, small businesses can streamline their operations, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the key principles of inventory management?
The key principles include maintaining accurate inventory records, optimizing inventory levels, implementing effective inventory control measures, and leveraging technology to automate and streamline processes.
What are the benefits of using inventory management software?
Inventory management software can help businesses automate inventory tracking, optimize stock levels, generate reports, and improve overall inventory management efficiency.
How can I optimize my inventory levels?
Inventory optimization involves finding the right balance between carrying too much or too little stock. Techniques include using safety stock calculations, forecasting demand, and implementing inventory optimization algorithms.
What are the best practices for inventory control?
Best practices include implementing physical inventory controls, such as cycle counting and regular audits, as well as establishing clear inventory policies and procedures.