Embark on a journey into the realm of business inventory accounting, a cornerstone of financial management. Accurate inventory accounting is paramount for businesses of all sizes, ensuring transparency, efficient operations, and informed decision-making.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of inventory valuation methods, management techniques, accounting systems, costing principles, and industry standards. Prepare to enhance your understanding and master the art of inventory accounting.
Business Inventory Accounting Definition and Overview

Business inventory accounting involves tracking and managing the stock of goods held by a business. Accurate inventory accounting is crucial for several reasons:
- Financial Reporting: Accurate inventory records are essential for preparing financial statements that reflect the true financial position of a business.
- Cost of Goods Sold: Inventory accounting helps determine the cost of goods sold, which directly impacts a company’s profitability.
- Taxation: Proper inventory accounting ensures compliance with tax regulations and helps businesses avoid overpaying or underpaying taxes.
Types of Business Inventory
Businesses maintain various types of inventory, including:
- Raw Materials: Materials used in the production process.
- Work-in-Progress (WIP): Partially completed products.
- Finished Goods: Completed products ready for sale.
- Merchandise: Goods purchased for resale without further processing.
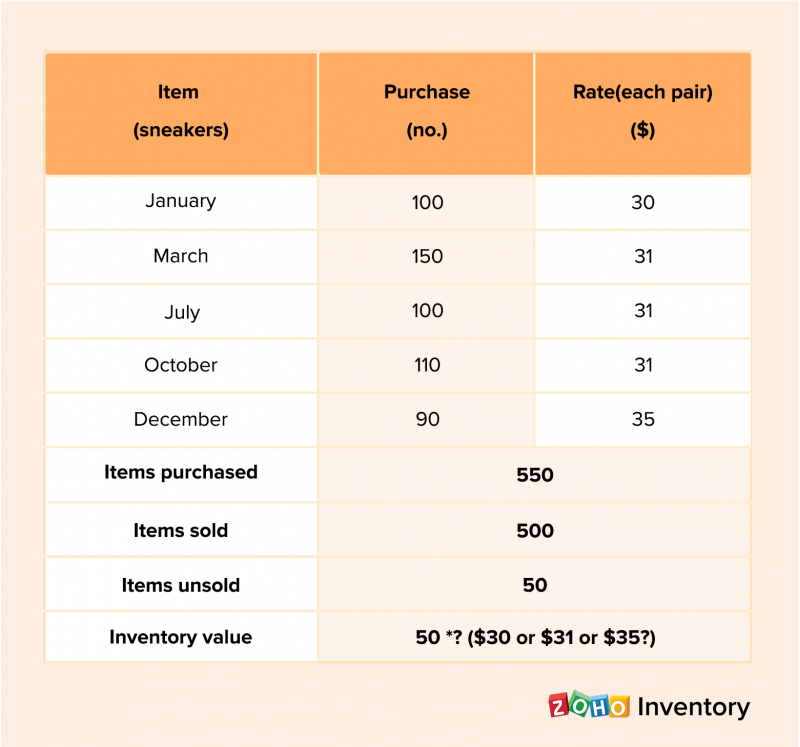
Inventory Valuation Methods

Inventory valuation methods are techniques used to determine the cost of inventory for financial reporting purposes. The choice of method can significantly impact a company’s financial statements, including its profitability and liquidity.The primary inventory valuation methods are:
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
- Weighted Average Cost
Inventory Management Techniques: Business Inventory Accounting
Effective inventory management is crucial for businesses to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Various techniques have been developed to improve inventory efficiency, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is a technique that categorizes inventory items based on their annual usage value. It divides items into three groups:
- A-items:High-value items that account for a significant portion of total inventory value and require close monitoring.
- B-items:Medium-value items that require moderate attention and can be managed with less frequent monitoring.
- C-items:Low-value items that represent a small portion of total inventory value and can be managed with minimal effort.
Benefits:
- Focuses resources on managing critical items.
- Reduces inventory carrying costs.
- Improves inventory turnover.
Drawbacks:
- Can be time-consuming to implement.
- Requires regular review and updating.
Example:A hardware store may use ABC analysis to identify high-value items like power tools (A-items), moderately valuable items like hammers (B-items), and low-value items like nails (C-items).
Just-in-Time Inventory (JIT)
JIT is an inventory management technique that aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when they are needed for production or sale. It focuses on eliminating waste and reducing carrying costs.
Benefits:
- Reduces inventory holding costs.
- Improves cash flow.
- Increases inventory turnover.
Drawbacks:
- Requires close coordination with suppliers.
- Can lead to production delays if suppliers fail to deliver on time.
Example:A manufacturing company may implement JIT to receive raw materials only when they are scheduled for production, reducing inventory levels and minimizing storage costs.
Inventory Accounting System
An inventory accounting system is a set of procedures and records used to track the flow of inventory through a business. It provides information about the quantity, cost, and location of inventory on hand. An effective inventory accounting system is essential for businesses to manage their inventory efficiently and avoid losses due to theft, damage, or obsolescence.
Components of an Inventory Accounting System
- Inventory records:These records contain information about the quantity, cost, and location of each item of inventory.
- Transaction documents:These documents record the movement of inventory into and out of the business. Examples of transaction documents include purchase orders, receiving reports, and shipping documents.
- Inventory control procedures:These procedures are designed to prevent and detect errors in the inventory accounting system. Examples of inventory control procedures include cycle counting and physical inventory counts.
How the System Tracks Inventory Transactions and Updates Inventory Records
When inventory is purchased, a purchase order is created. The purchase order is used to track the order until the inventory is received. When the inventory is received, a receiving report is created. The receiving report is used to update the inventory records and to create a vendor invoice.
When inventory is sold, a shipping document is created. The shipping document is used to update the inventory records and to create a customer invoice.
Importance of Internal Controls in Inventory Accounting, Business inventory accounting
Internal controls are important in inventory accounting because they help to prevent and detect errors and fraud. Examples of internal controls in inventory accounting include:
- Segregation of duties:This means that different employees are responsible for different parts of the inventory accounting process. For example, one employee may be responsible for purchasing inventory, while another employee is responsible for receiving inventory.
- Physical inventory counts:These are periodic counts of the inventory on hand. Physical inventory counts are used to verify the accuracy of the inventory records.
- Cycle counting:This is a process of counting a portion of the inventory on a regular basis. Cycle counting is used to identify errors in the inventory records before they become significant.
Inventory Costing and Reporting
Inventory costing is a crucial process in accounting that involves assigning costs to the inventory items held by a business. It directly impacts the financial statements, including the balance sheet and income statement, as it determines the value of inventory assets and the cost of goods sold (COGS).Inventory costing helps businesses track the cost of inventory items throughout their lifecycle, from acquisition to sale.
It ensures that the cost of goods sold is accurately reflected in the financial statements, providing a clear picture of the company’s profitability and financial performance.
Inventory Costing Methods
There are several inventory costing methods used by businesses, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include:
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
This method assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first. As a result, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the earliest purchases. FIFO tends to result in higher COGS and lower ending inventory values during periods of rising prices.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
This method assumes that the most recently purchased inventory items are sold first. Consequently, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the latest purchases. LIFO tends to result in lower COGS and higher ending inventory values during periods of rising prices.
Weighted Average Cost
This method calculates the average cost of inventory items based on the cost of all purchases made during a specific period. The average cost is then used to assign costs to the items sold. Weighted average cost tends to result in COGS and ending inventory values that fall between FIFO and LIFO.The choice of inventory costing method depends on several factors, including the nature of the business, industry practices, and tax implications.
It is important to select a method that aligns with the business’s accounting policies and provides a fair and accurate representation of inventory costs.
Impact on Financial Statements
Inventory costing has a significant impact on financial statements. The cost of goods sold, calculated using the chosen inventory costing method, is a major expense on the income statement. It directly affects the gross profit and net income of the business.Additionally, the value of ending inventory, determined using the inventory costing method, is reported as an asset on the balance sheet.
This value impacts the calculation of current assets, working capital, and overall financial ratios.By accurately assigning costs to inventory items, inventory costing provides valuable insights into the cost structure of the business, its profitability, and its financial health. It enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding inventory management, pricing strategies, and overall financial planning.
Inventory Accounting Standards
Inventory accounting is a vital component of financial reporting, and as such, it is subject to various accounting standards. These standards aim to ensure consistency and transparency in the reporting of inventory, facilitating comparability and reliability of financial statements.The two most widely recognized sets of accounting standards are the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
IFRS is issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), while GAAP is developed by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the United States.Both IFRS and GAAP provide guidance on the valuation, recognition, and disclosure of inventory. The key requirements and principles of these standards include:
- Inventory Valuation:IFRS and GAAP require that inventory be valued at the lower of cost or net realizable value (NRV). Cost can be determined using various methods, such as first-in, first-out (FIFO), last-in, first-out (LIFO), or weighted average cost.
- Inventory Recognition:Inventory is recognized when it is acquired and meets the definition of an asset, which means it is controlled by the entity and is expected to provide future economic benefits.
- Inventory Disclosure:IFRS and GAAP require that companies disclose significant information about their inventory, including the valuation method used, the amount of inventory held, and any write-downs or impairments that have been recognized.
The accounting standards related to inventory accounting have a significant impact on inventory accounting practices. They provide a framework for companies to follow when recording and reporting inventory, ensuring consistency and comparability. This allows users of financial statements to better understand and compare the financial performance of different companies.
Last Recap
In conclusion, business inventory accounting plays a vital role in ensuring financial accuracy, optimizing inventory management, and meeting regulatory requirements. By embracing the concepts and techniques Artikeld in this guide, businesses can gain a competitive edge, streamline operations, and make informed decisions that drive growth and profitability.
Question Bank
What is the purpose of inventory accounting?
Inventory accounting provides a systematic approach to recording, valuing, and reporting inventory transactions, ensuring accurate financial statements and efficient inventory management.
Which inventory valuation method is most appropriate for my business?
The choice of inventory valuation method depends on factors such as industry practices, inventory turnover rate, and desired financial reporting outcomes. FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average cost are commonly used methods.
How can I improve inventory management efficiency?
Implementing techniques such as ABC analysis, just-in-time inventory, and safety stock management can optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and enhance operational efficiency.