Business inventory figures are essential for businesses of all sizes to track and manage their stock effectively. By understanding the concept of inventory figures, businesses can gain valuable insights into their inventory levels, optimize their inventory management strategies, and improve their overall profitability.
This comprehensive guide will provide you with an in-depth understanding of business inventory figures, including different inventory management methods, valuation techniques, analysis metrics, control systems, forecasting methods, optimization strategies, reporting tools, and inventory management software.
Business Inventory Figures Overview
Business inventory figures represent the total value of all goods held by a business for sale or use in production. They provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health, operational efficiency, and overall performance.
Examples of inventory figures include raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished goods. Tracking inventory figures is crucial for several reasons:
- Cost Management:Inventory figures help businesses optimize their inventory levels, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking, leading to cost savings.
- Sales Forecasting:By analyzing inventory turnover rates and demand patterns, businesses can forecast future sales and plan production accordingly.
- Supply Chain Management:Inventory figures enable businesses to manage their supply chains effectively, ensuring the timely delivery of goods and avoiding disruptions.
- Financial Reporting:Inventory figures are reported on a company’s balance sheet and are used to calculate important financial ratios, such as inventory turnover ratio and days sales in inventory.
Inventory Management Methods: Business Inventory Figures
Inventory management methods are crucial for businesses to optimize stock levels, minimize costs, and enhance operational efficiency. Various methods exist, each with its advantages and disadvantages, and selecting the appropriate method is essential for different business needs.
FIFO (First-In, First-Out)
- Assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first.
- This method aligns with the physical flow of inventory in many businesses.
- In periods of rising prices, FIFO results in lower cost of goods sold (COGS) and higher ending inventory value.
- Can be more complex to implement in practice, especially for businesses with diverse inventory items.
LIFO (Last-In, First-Out)
- Assumes that the most recently purchased inventory items are sold first.
- In periods of rising prices, LIFO results in higher COGS and lower ending inventory value compared to FIFO.
- Can be beneficial for tax purposes in some jurisdictions.
- May not accurately reflect the physical flow of inventory and can lead to distortions in financial statements.
Weighted Average
- Calculates the average cost of inventory items based on their purchase prices and quantities.
- Provides a more stable COGS and ending inventory value compared to FIFO and LIFO.
- Easier to implement and manage than FIFO or LIFO.
- May not accurately reflect the actual cost of goods sold, especially in periods of significant price fluctuations.
Choosing the Appropriate Method
The choice of inventory management method depends on several factors, including:
- Nature of the business and its inventory items
- Physical flow of inventory
- Tax implications
- Desired level of cost stability
- Complexity of implementation and management
Businesses should carefully consider these factors and consult with accounting professionals to determine the most suitable inventory management method for their specific needs.
Inventory Valuation
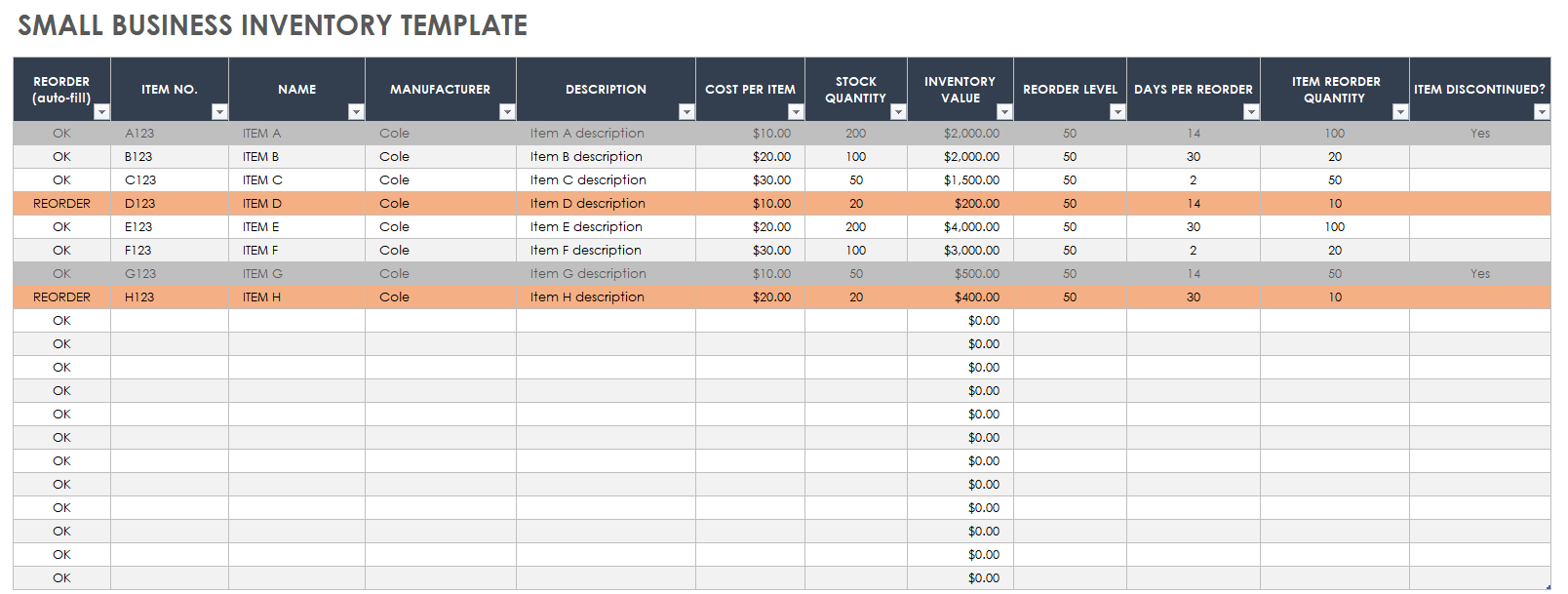
Inventory valuation is a critical aspect of financial reporting, as it directly impacts the reported value of assets and, consequently, the overall financial health of a business. Understanding the different methods used to value inventory is essential for ensuring accurate financial statements and making informed business decisions.
There are several methods available for valuing inventory, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include:
Cost-Based Valuation Methods
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO):This method assumes that the first items purchased are the first to be sold. Therefore, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the oldest inventory on hand.
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO):This method assumes that the last items purchased are the first to be sold. As a result, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the most recent inventory acquired.
- Weighted Average Cost:This method calculates the average cost of all inventory items on hand. This average cost is then used to determine the cost of goods sold.
Market-Based Valuation Methods
- Lower of Cost or Market (LCM):This method values inventory at the lower of its cost or its current market value. The rationale behind this method is to ensure that the reported value of inventory does not exceed its realizable value.
- Net Realizable Value (NRV):This method values inventory at its estimated selling price, less any estimated costs to complete and sell the inventory.
Impact of Valuation Methods on Financial Statements
The choice of inventory valuation method can have a significant impact on the financial statements. For example, FIFO tends to result in higher cost of goods sold and lower net income during periods of rising prices, while LIFO has the opposite effect.
LCM can result in write-downs of inventory value during periods of falling prices, which can reduce net income and retained earnings.
Selecting the Appropriate Valuation Method, Business inventory figures
The selection of the appropriate inventory valuation method depends on several factors, including:
- Nature of the inventory
- Industry practices
- Financial reporting objectives
- Tax implications
It is important to note that the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) require the use of the lower of cost or market (LCM) method for inventory valuation. However, U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) allow companies to choose from a variety of methods, including FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average cost.
Inventory Analysis
Inventory analysis involves examining inventory data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. It helps businesses optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency.
Key metrics used in inventory analysis include:
- Inventory Turnover Ratio: Measures how efficiently inventory is being sold and replaced. A higher ratio indicates faster inventory turnover and lower carrying costs.
- Days Sales in Inventory (DSI): Indicates the average number of days it takes to sell the current inventory. A lower DSI suggests efficient inventory management.
By interpreting inventory analysis results, businesses can:
- Identify slow-moving or obsolete inventory that needs to be cleared out.
- Determine optimal inventory levels to avoid stockouts or excess inventory.
- Reduce inventory carrying costs by optimizing storage and handling practices.
- Improve customer service by ensuring availability of products.
For example, a company with a low inventory turnover ratio may have excess inventory, leading to higher storage costs and potential obsolescence. By analyzing this metric, the company can identify the root cause and take corrective actions to improve inventory efficiency.
Inventory Control
Inventory control is a crucial aspect of inventory management, ensuring the optimal balance of stock levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs. Effective inventory control helps businesses prevent stockouts, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency.
Safety Stock
Safety stock refers to the extra inventory held beyond the average demand to buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply chain disruptions. Maintaining adequate safety stock levels helps businesses mitigate the risk of stockouts and ensures customer satisfaction.
Reorder Point
The reorder point is the inventory level at which a new order should be placed to replenish stock. It is calculated based on factors such as average demand, lead time, and safety stock levels. By setting an appropriate reorder point, businesses can avoid stockouts while minimizing excess inventory.
Other Inventory Control Techniques
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO):This method assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, ensuring a consistent flow of goods.
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO):This method assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first, potentially resulting in higher inventory valuation during inflationary periods.
- Just-In-Time (JIT):This inventory management philosophy aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when they are needed for production or sale.
Inventory Forecasting

Inventory forecasting is crucial for businesses to optimize inventory levels, prevent stockouts, and reduce waste. It involves predicting future demand to ensure the right amount of inventory is available at the right time.There are various inventory forecasting methods, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
Time series analysis uses historical data to identify patterns and trends, while demand forecasting considers external factors like market conditions and consumer behavior. The appropriate forecasting method depends on the specific industry, product characteristics, and data availability.
Selecting the Forecasting Method
Choosing the appropriate forecasting method involves considering factors such as:
- Data availability and quality
- Product demand patterns
- Lead times and supply chain constraints
- Accuracy requirements
- Computational resources
By carefully selecting and implementing an effective inventory forecasting method, businesses can improve inventory management, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization is the process of managing inventory levels to minimize costs while maintaining customer service levels. It involves finding the balance between holding too much inventory, which can lead to waste and obsolescence, and holding too little inventory, which can result in stockouts and lost sales.
There are a number of different inventory optimization techniques that can be used, including:
- Just-in-time (JIT) inventory:JIT is a manufacturing philosophy that seeks to eliminate waste by producing only the inventory that is needed, when it is needed. This can help to reduce inventory carrying costs and improve cash flow.
- Vendor-managed inventory (VMI):VMI is a partnership between a retailer and a supplier in which the supplier manages the retailer’s inventory. This can help to improve inventory accuracy and reduce stockouts.
- Safety stock:Safety stock is a buffer of inventory that is held to protect against unexpected demand or supply disruptions. The amount of safety stock that is needed will vary depending on the product and the level of demand.
Inventory optimization can be a complex process, but it can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line. By implementing effective inventory optimization strategies, companies can reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase profitability.
Inventory Reporting
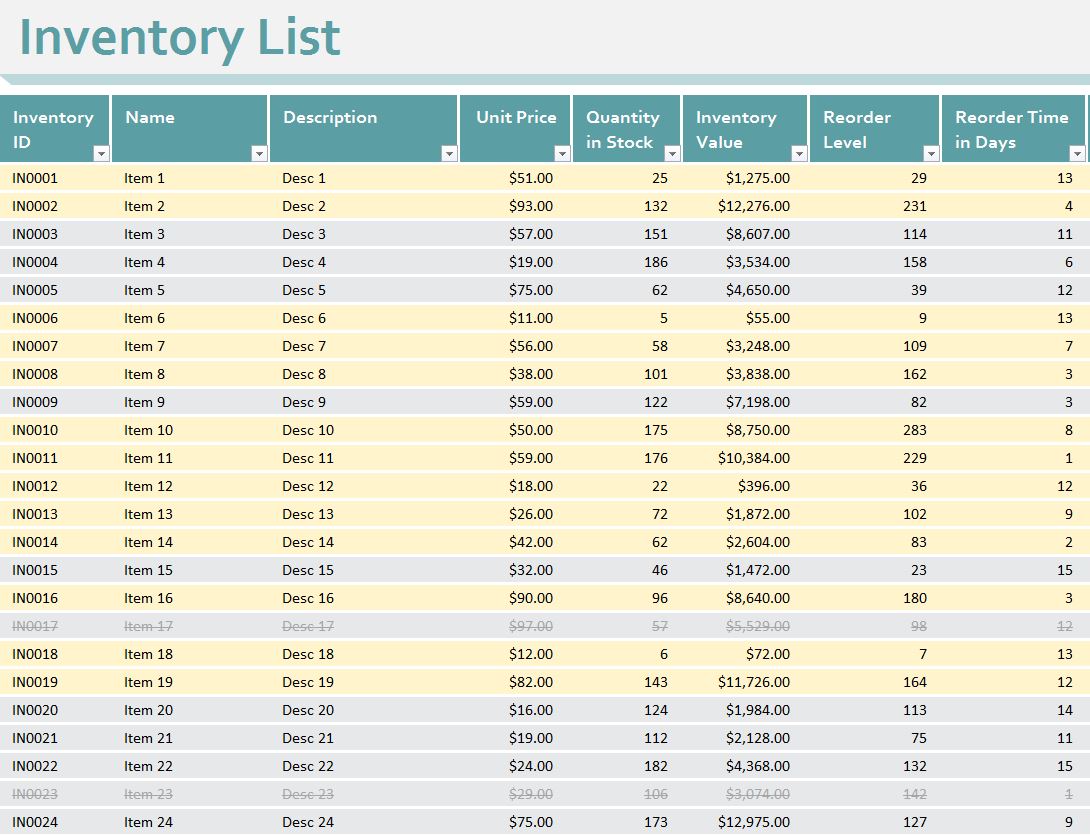
Inventory reporting is a crucial aspect of inventory management that provides valuable insights into the status, movement, and efficiency of inventory operations. These reports help businesses make informed decisions about inventory levels, purchasing, and resource allocation.
Key Inventory Reports
- Inventory Balance Report:This report provides a snapshot of the inventory on hand at a specific point in time. It lists the quantity and value of each item in stock, allowing businesses to track inventory levels and identify potential shortages or surpluses.
- Inventory Turnover Report:This report measures how quickly inventory is sold and replaced. It calculates the number of times inventory is turned over during a given period, indicating the efficiency of inventory management and the ability to meet customer demand.
Using Inventory Reports for Informed Decision-Making
Inventory reports empower businesses to make informed decisions by providing:
- Visibility into Inventory Levels:Reports help businesses monitor inventory levels, ensuring they have enough stock to meet customer demand without overstocking.
- Identification of Slow-Moving Items:By analyzing inventory turnover, businesses can identify slow-moving items that may be tying up resources and contributing to carrying costs.
- Optimization of Purchasing:Inventory reports provide insights into purchasing patterns and help businesses optimize their ordering strategies to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes. It can help businesses track their inventory levels, manage their supply chain, and make better decisions about their inventory.
There are many different types of inventory management software available, each with its own unique features and benefits. Some of the most common types of inventory management software include:
- Cloud-based inventory management softwareis hosted on a remote server and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This type of software is often more affordable than on-premise inventory management software and is a good option for businesses that do not have the resources to invest in a dedicated server.
- On-premise inventory management softwareis installed on a local server and is not accessible from outside the business’s network. This type of software is more expensive than cloud-based inventory management software but offers more control and security.
When selecting an inventory management software, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The size of your business
- The complexity of your inventory
- Your budget
- Your IT resources
Once you have selected an inventory management software, it is important to implement it correctly. This involves training your staff on how to use the software and setting up the software to meet your specific needs.
Inventory management software can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes. By using inventory management software, businesses can improve their inventory management practices and make better decisions about their inventory.
Case Studies
Businesses across industries have successfully implemented inventory management best practices, leading to improved efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Here are a few notable case studies:
Amazon
- Implemented a sophisticated inventory management system that leverages data analytics, machine learning, and robotics to optimize inventory levels.
- Reduced inventory carrying costs by 25% while maintaining high levels of customer service.
- Improved inventory accuracy by 99%, reducing the incidence of stockouts and overstocking.
Walmart
- Deployed a cross-docking strategy to reduce inventory holding time and transportation costs.
- Utilized RFID technology to improve inventory visibility and reduce shrinkage.
- Reduced inventory levels by 15% while increasing sales by 5%, demonstrating the effectiveness of lean inventory management.
Toyota
- Implemented the “Just-in-Time” inventory system, which minimizes inventory levels and relies on close coordination with suppliers.
- Reduced inventory carrying costs by 50% and improved production efficiency.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction by reducing lead times and improving product quality.
Last Point
In conclusion, business inventory figures are a critical aspect of inventory management that can significantly impact a business’s financial performance. By implementing effective inventory management practices, businesses can optimize their stock levels, reduce costs, improve customer service, and gain a competitive advantage.
Popular Questions
What are the different types of inventory management methods?
There are several inventory management methods, including FIFO (First-In, First-Out), LIFO (Last-In, First-Out), and weighted average.
What is the importance of inventory valuation?
Inventory valuation is important because it determines the value of your inventory on your financial statements, which can impact your profitability and tax liability.
How can inventory analysis help improve business performance?
Inventory analysis can help businesses identify trends, optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and improve customer service.