Business inventory for liquor stores – Welcome to the ultimate guide to business inventory management for liquor stores. In this comprehensive resource, we’ll delve into the intricacies of effective inventory management, empowering you to optimize your stock levels, minimize losses, and maximize profits.
Whether you’re a seasoned liquor store owner or just starting out, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and strategies you need to establish a robust inventory management system that will drive your business to success.
Inventory Management for Liquor Stores

Effective inventory management is crucial for liquor stores to maintain profitability, prevent stockouts, and meet customer demand. Implementing the right strategies can help optimize inventory levels, reduce waste, and enhance overall store operations.
Inventory Control and Preventing Stockouts, Business inventory for liquor stores
Maintaining accurate inventory records is essential to prevent stockouts. Utilize inventory management software or a spreadsheet to track inventory levels in real-time. Conduct regular inventory counts to identify discrepancies and adjust records accordingly. Establish minimum stock levels for each item to ensure adequate inventory without overstocking.
Optimizing Inventory Levels
Optimizing inventory levels requires balancing customer demand with storage capacity and financial constraints. Utilize historical sales data to forecast demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. Consider seasonal fluctuations and special events that may impact demand. Implement a safety stock level to buffer against unexpected demand spikes.
Inventory Categorization and Organization
An efficient liquor store inventory system requires a well-organized and categorized approach. This involves classifying and grouping liquor products based on specific criteria to streamline storage, tracking, and retrieval.
SKU and Barcode Utilization
Utilizing Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) and barcodes is crucial for efficient inventory management. SKUs are unique identifiers assigned to each product, while barcodes provide a machine-readable representation of these SKUs. This system enables quick and accurate identification, tracking, and scanning of inventory items, reducing manual errors and streamlining the inventory process.
Inventory Database Creation
Creating a user-friendly inventory database is essential for effective inventory management. This database should include comprehensive information on each product, such as product name, SKU, barcode, quantity on hand, reorder point, supplier details, and pricing. A well-structured database allows for easy data entry, retrieval, and reporting, providing valuable insights into inventory levels and trends.
Inventory Tracking and Monitoring
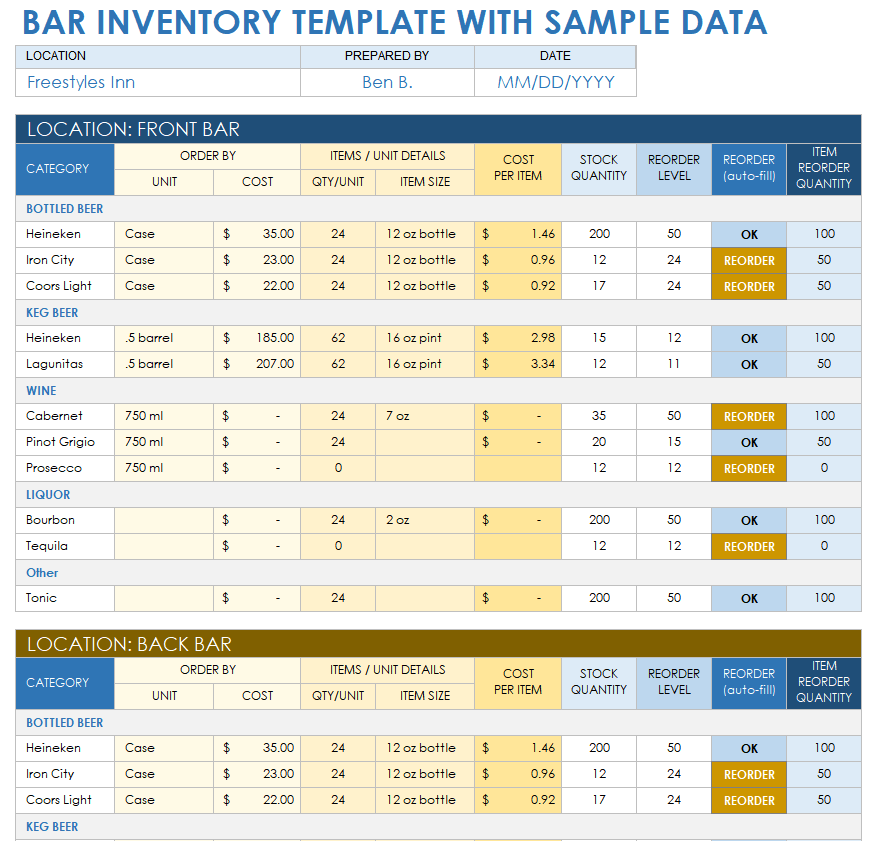
Effective inventory tracking and monitoring are crucial for liquor stores to maintain optimal stock levels, prevent overstocking or shortages, and ensure efficient operations. This involves implementing robust methods for tracking inventory levels in real-time, utilizing inventory management software, and employing techniques to monitor inventory movement and identify trends.
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
- Manual Inventory Counts:Regular physical inventory counts provide accurate data on stock levels but can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Technology:RFID tags attached to inventory items enable real-time tracking using RFID readers, providing instant updates on stock levels.
- Barcode Scanning:Barcodes on inventory items allow for quick and accurate scanning, facilitating real-time inventory updates through barcode scanners.
- POS (Point of Sale) Systems:POS systems integrated with inventory management software automatically update inventory levels based on sales transactions.
Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software provides comprehensive tools for managing inventory levels, tracking stock movement, and generating reports. Key advantages include:
- Centralized Inventory Management:Software consolidates inventory data from multiple locations, providing a single, real-time view of stock levels.
- Automated Inventory Updates:Software automatically updates inventory levels based on sales, purchases, and adjustments, reducing manual errors.
- Reorder Point Management:Software sets reorder points based on historical demand and lead times, ensuring timely replenishment of stock.
- Inventory Forecasting:Software analyzes historical data to forecast future demand, helping businesses optimize inventory levels and avoid overstocking.
Monitoring Inventory Movement and Trends
Tracking inventory movement and identifying trends helps businesses understand demand patterns, optimize stock levels, and prevent wastage. Techniques include:
- Inventory Turnover Analysis:Calculating inventory turnover ratio (cost of goods sold / average inventory) provides insights into how quickly inventory is sold and replaced.
- Trend Analysis:Tracking inventory levels over time reveals patterns in demand, enabling businesses to anticipate future requirements.
- ABC Analysis:Categorizing inventory items based on their value and usage helps prioritize inventory management efforts, focusing on high-value items.
- Cycle Counting:Regular partial inventory counts verify inventory accuracy and identify potential discrepancies, reducing the risk of inventory shrinkage.
Inventory Replenishment and Forecasting
Inventory replenishment involves monitoring inventory levels and placing orders to ensure adequate stock. Effective replenishment is crucial for meeting customer demand, preventing stockouts, and optimizing cash flow.
Forecasting future demand is essential for optimal replenishment. Various methods exist, including historical data analysis, seasonal patterns, and predictive analytics. Accurate forecasting helps businesses maintain optimal stock levels, minimizing overstocking and understocking.
Demand Forecasting Methods
- Historical Data Analysis:Examining past sales data to identify trends and patterns in demand.
- Seasonal Patterns:Identifying and incorporating seasonal fluctuations into demand forecasts.
- Predictive Analytics:Using statistical models and machine learning algorithms to predict future demand based on historical data and other factors.
Managing Seasonal Fluctuations
Seasonal demand variations require specific strategies for inventory management. Businesses can:
- Adjust Replenishment Frequency:Increase orders during peak seasons and reduce them during off-seasons.
- Offer Promotions and Discounts:Encourage sales during off-seasons to reduce excess inventory.
- Collaborate with Suppliers:Negotiate flexible delivery schedules to accommodate seasonal fluctuations.
Inventory Audits and Reconciliation: Business Inventory For Liquor Stores
Regular inventory audits and reconciliation are crucial for liquor stores to maintain accurate inventory records, minimize losses, and optimize operations. By conducting audits, businesses can identify discrepancies, prevent shrinkage, and ensure that inventory levels align with actual stock.
Steps Involved in Conducting an Inventory Audit
- Plan the Audit:Determine the scope, schedule, and resources needed for the audit.
- Train Auditors:Ensure auditors are familiar with inventory procedures and reconciliation techniques.
- Count Inventory:Conduct a thorough physical count of all inventory items, including on-hand stock, backstock, and items in transit.
- Reconcile Counts:Compare the physical count to the inventory records to identify discrepancies.
- Analyze Discrepancies:Investigate the causes of discrepancies, such as theft, breakage, or errors in counting.
- Resolve Discrepancies:Take corrective actions to adjust inventory records and prevent future discrepancies.
- Document the Audit:Create a detailed report documenting the audit process, findings, and recommendations.
Methods for Identifying and Resolving Inventory Discrepancies
- Cycle Counting:Regular audits of a portion of the inventory to identify and correct discrepancies early on.
- Spot Checks:Random audits of specific items or areas to detect potential issues.
- Variance Analysis:Comparing actual inventory levels to expected levels to identify trends and patterns in discrepancies.
- Vendor Reconciliation:Matching purchase orders and invoices with inventory records to identify discrepancies in received and recorded inventory.
Inventory Valuation and Reporting
Inventory valuation methods determine the value of inventory for financial reporting purposes. Common methods include:
First-in, first-out (FIFO)
Assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, resulting in higher cost of goods sold (COGS) during periods of inflation.
Last-in, first-out (LIFO)
Assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first, resulting in lower COGS during periods of inflation.
Weighted average cost
Calculates the average cost of inventory based on all purchases made during a period, resulting in a stable COGS.The choice of valuation method impacts the financial statements, as it affects COGS and ending inventory values.
Inventory Reports
Inventory reports provide valuable information for decision-making and analysis, such as:
Inventory turnover
Measures the rate at which inventory is sold and replaced, indicating efficiency of inventory management.
Days sales in inventory (DSI)
Calculates the average number of days inventory is held before being sold, indicating potential inventory issues.
Stockout analysis
Identifies items that frequently run out of stock, allowing for proactive replenishment strategies.Creating informative inventory reports involves:
Selecting relevant data
Include key metrics such as inventory levels, COGS, and sales figures.
Organizing data clearly
Present data in a logical and easy-to-understand format, using tables, charts, and graphs.
Highlighting trends and exceptions
Draw attention to significant changes or anomalies in inventory levels or performance.
Providing actionable insights
Include recommendations or suggestions based on the analysis of inventory data.
Closing Notes
By implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you’ll gain a competitive edge in the liquor industry, ensuring that your store is always stocked with the right products at the right time. Remember, inventory management is not just about tracking stock; it’s about optimizing your entire supply chain, reducing costs, and ultimately increasing your bottom line.
Common Queries
What are the key principles of effective inventory management for liquor stores?
Effective inventory management for liquor stores involves maintaining optimal stock levels, minimizing stockouts, categorizing and organizing inventory efficiently, tracking inventory levels in real-time, and conducting regular inventory audits.
How can I optimize inventory levels to meet customer demand?
To optimize inventory levels, liquor store owners should analyze sales data, forecast future demand, and establish safety stock levels. Additionally, implementing a perpetual inventory system can provide real-time visibility into stock levels.
What are the benefits of using SKUs and barcodes for liquor store inventory?
SKUs (Stock Keeping Units) and barcodes streamline inventory tracking, reduce errors, and facilitate efficient stock replenishment. They enable quick and accurate identification of products, making it easier to manage stock levels and prevent stockouts.